Pump Efficiency Basics: How to Measure, Improve, and Maintain Performance
Understanding Pump Efficiency and Its Importance
Pump efficiency is a critical metric that shows how effectively a pump converts energy into hydraulic force. Higher efficiency means lower energy costs, longer pump life, and reduced environmental impact. In most applications, centrifugal pumps achieve efficiencies between 50 and 93 percent, depending on design and system conditions, as explained in this overview from Linquip.
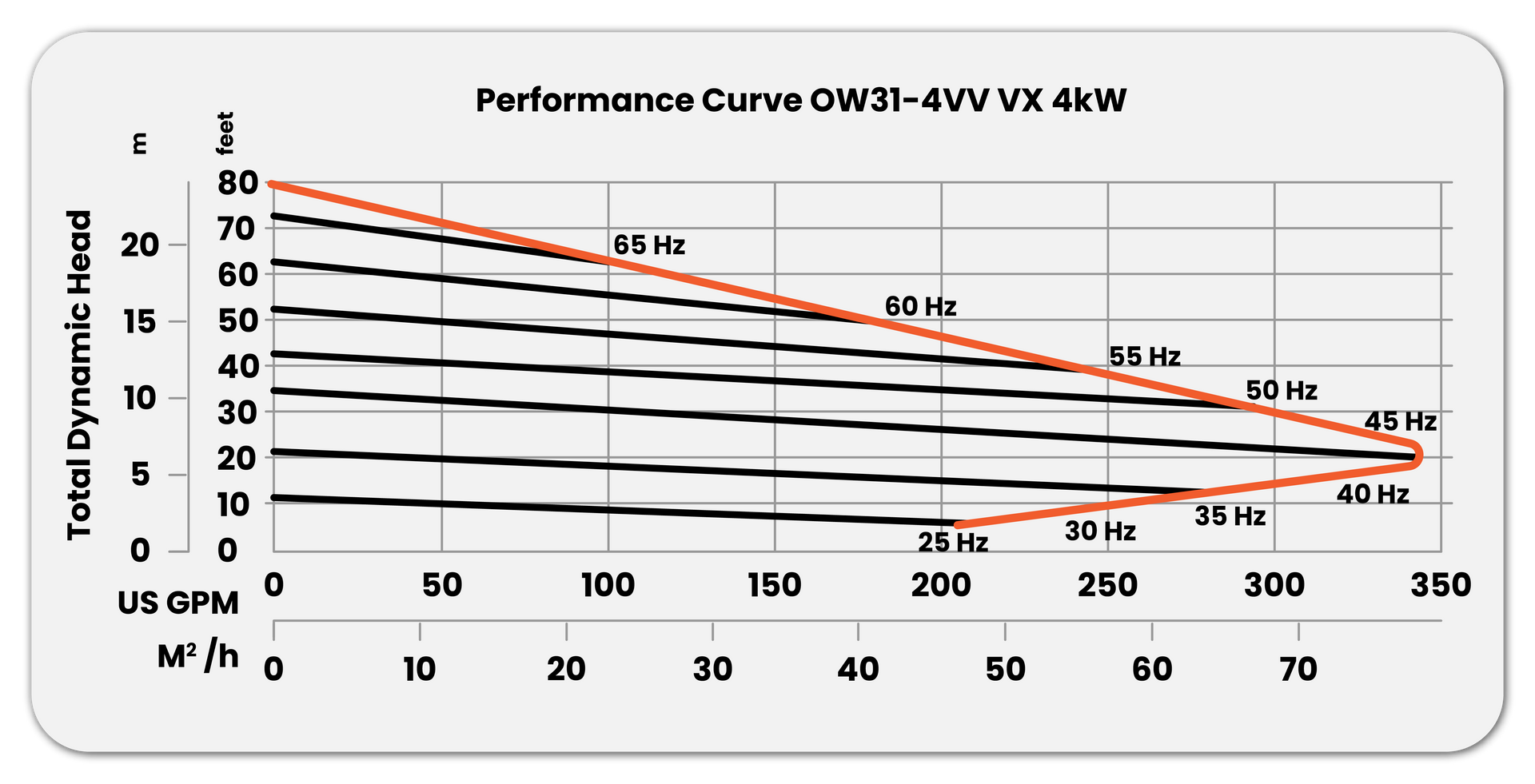
Calculating Centrifugal Pump Efficiency
Efficiency Formula
To calculate pump efficiency (η), use the formula:
η = (Hydraulic Power Output ÷ Power Input) × 100%
Hydraulic power is based on flow rate, total head, fluid density, and gravity. Power input is the electrical power or brake horsepower consumed by the pump.
A helpful guide from
Pumps Blog walks through this formula and explains how to measure each variable in the field.
Practical Example
For example, if a pump delivers 90 gallons per minute (GPM) at 35 feet of head and uses 1 BHP, the efficiency would be:
η = [(90 × 35) ÷ 3960] ÷ 1 × 100 ≈ 79.5%
This calculation is also visualized using tools like the True Geometry centrifugal pump calculator.

Factors Affecting Pump Efficiency
Hydraulic, Mechanical, and Volumetric Efficiency
Pump efficiency is a combination of:
- Hydraulic efficiency, affected by impeller design and flow conditions
- Mechanical efficiency, impacted by bearing friction and seal performance
- Volumetric efficiency, reduced by internal leakage or worn clearances
You can explore these distinctions further in Water and Wastewater’s breakdown and Short Engineering Courses’ overview.
Common Causes of Efficiency Loss
Several conditions cause pumps to lose efficiency:
- Operating away from the Best Efficiency Point (BEP): This increases hydraulic losses and vibration
- Impeller wear: Reduces flow capacity and alters pressure output
- Cavitation: Causes internal damage due to vapor bubble collapse
- Air entrainment: Introduces inefficiencies through flow disruption
Pumps Blog offers a great resource on identifying and correcting these problems.

Strategies to Improve Pump Efficiency
Regular Maintenance
Routine inspections and service extend pump life and help maintain design performance. Tracking wear, alignment, and seal condition are key to keeping systems efficient.
Impeller Trimming and Speed Control
Trimming the impeller diameter or using a variable speed drive (VSD) can better match pump output to system demand. Pumps Blog outlines how these adjustments reduce energy waste in oversized systems.
System Design Optimization
Reducing friction losses and avoiding sharp bends or undersized piping helps minimize energy waste. Many energy audits reveal that correcting piping layout improves pump efficiency as much as replacing hardware.
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal Performance
Using performance curves and historical operating data helps track efficiency over time. When deviations appear in flow, pressure, or power draw, it’s a signal that realignment or repair may be needed. This type of predictive maintenance, as discussed in Linquip’s performance guide, is becoming standard practice in industrial operations.

How Rhino Pumps Can Assist
At Rhino Pumps, we specialize in maximizing system performance through engineering expertise, rebuild services, and retrofits. Whether you’re dealing with oversized equipment, cavitation loss, or aging components, we can help you:
- Evaluate existing systems for efficiency bottlenecks
- Recommend pump upgrades, controls, or modifications
- Supply wear-resistant components to minimize performance loss
- Deliver tailored solutions that reduce operating costs over time
Contact Rhino Pumps to schedule an efficiency consultation or system review.